Airplane Drag - This is the second part of this two part series about the four flight forces that we will introduce and draw. Here you can lift and find our weights. William Kershner's Student Flight Manual explains the pilot's desire to deploy and draw:
The blower is equipped with a propeller or a jet. however, here is the most important thing for you.
Airplane Drag
The theory of propellants is quite complex, but Newton's idea of "equal and opposite" can be expressed here.
Forces Acting On The Aircraft
The propeller picks up a large air mass and accelerates the collector, traveling through an equal and opposite reaction plane.
Maybe it's time to clean up a few words like "force" and "strength". Sent
Can be defined as tension, pressure or weight. You don't need to move anything; you can apply a force to a very heavy object and nothing will move. Or it can apply less force and move. It moves when something has a force;
A common measure of power is the horsepower name. The bird develops horsepower in its cylinders and turns it into motion. In straight and straight, single-speed, legan flight, the thrust developed (pounds) is assumed to be equal to the drag of an airplane.
Nasa Seeks It All: High Lift, Low Drag
When a body moves in a fluid (such as air), friction is produced. They pull parallel and in the same direction as the relative wind. The "all" drag of the aircraft consists of two types.
- drag consists of (1) "shape drag" (airport and radio antennas, shape of wings, fuselage, etc.), (2) surface friction, and (3) mixing of airflow between parts (as will be found). wings, body, or combination of trunk and tail). Since the term "parasite" means, this type of drag benefits no one and is more popular than any other parasite. And as the square of the airspeed increases, the drag increases. Double the airspeed and the parasitic drag increases
This is the pull from lifting. The relative wind is deflected downward from the wing and gives a reward component called the lift vector.
(The vector of life is the yoke of the train). The air above each wing tip moves below the pressure peak and eddies form in the wing that exert forces proportional to the amount of drag available. The strength (and drag) of these eddies increase significantly at higher angles of attack. When two masses are in contact, they resist each other's movement. The air in the boat resists the forward motion of the aircraft. So when it comes to flight, resistance is the movement of the aircraft in the air. They attract, they oppose, they push.
Why Airlines Hate Squished Bugs On Airplane Wings
Drag is created by mixing airflow lines between airframe components. For example, wing and fuselage or pier and fuselage strut gear. As the air flows and mixes around the various parts of the aircraft, a local shock wave is created and the total drag is greater than the drag the parts would have on their own.
Skin friction friction is a result of the rough surface of the aircraft. Olympic swimmers wear caps on their heads to avoid extra hair growth and to swim faster in the water. The same principle can be applied to most aircraft where the smooth surface reduces drag surface friction, increasing performance and fuel efficiency.
The figure draws the effect of the common object relative to the relative wind. Have you ever stretched your hand out of the car window, first straight, then vertically into the wind? When your hand is horizontal like a sash, it's easy to get out of the window. But when you open your hand to the wind, your hand flies back and requires a lot of force to hold it in place. This is the easiest way to draw it.
Air (and eddies) roll down the back of your wing, so they're controlled in what's known as a downdraft. Downstream indicates the relative wind direction, the more downstream there is, the more downstream. This is important for a very good reason: always lift perpendicular to the relative wind.
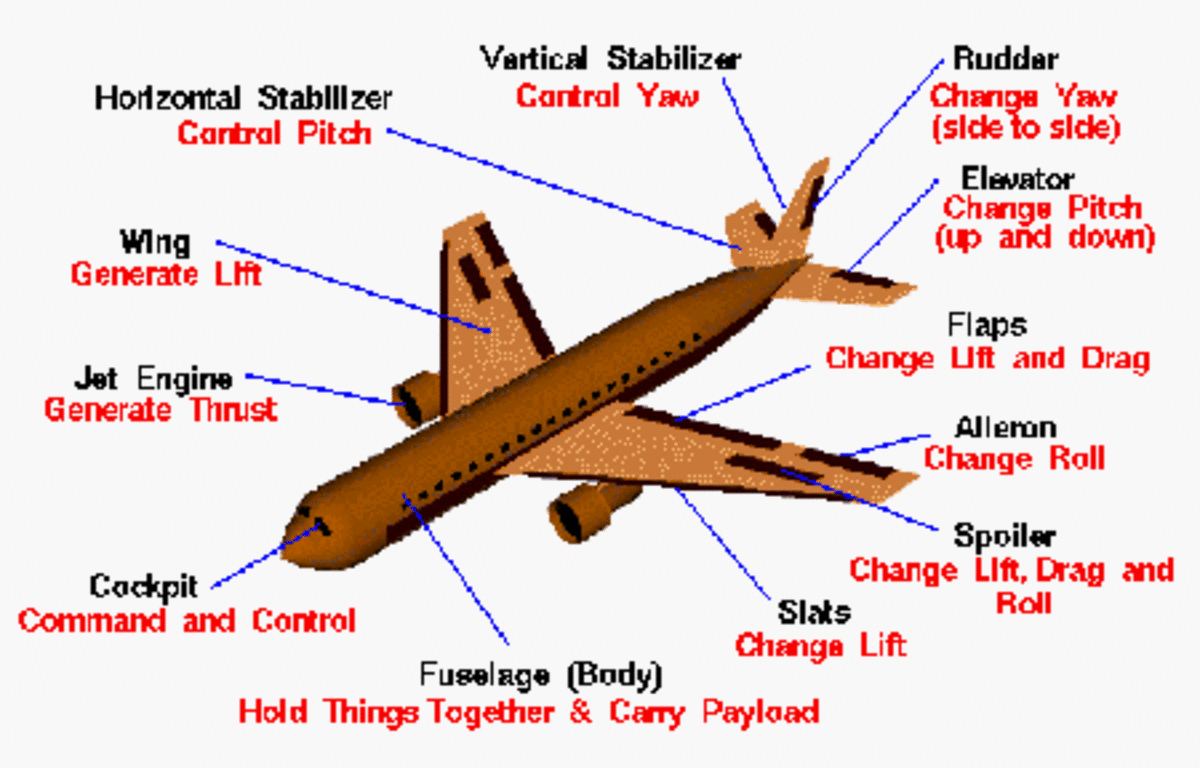
Aircraft Flight Controls
Check out the figure below. You can see that when you have less downstream, you have more downstream, the vector pulls back more points, causing drag to be induced. On top of that, it takes energy from your wings to create a downward current and vortex, which creates drag.
As you approach the floor, the wash decreases downwards and the eddies that are reduced and brought back by you are reduced. Click here to learn everything you need to know about the world impact.
A drag wave is caused by the generation of shock waves around an aircraft in transonic or supersonic flight. As the air flows from the supersonic region before the shock to the subsonic region after the shock, it separates and becomes turbulent. As the shock wave gets stronger, more distortion, known as drag waves, is produced.

Swayne is an editor, certified flight instructor, and first officer on the Boeing 757/767 for a major US carrier. Graduated from the University of North Dakota in 2018 with an aeronautical degree, holds a PIC Type Rating for Cessna Citation Jets (CE-525), is a former pilot at Mokulele Airlines, and flew Embraer 145s early in his airline career. Swayne is the author of weekly articles, quizzes and charts. You can join Swayne and follow his flying adventures on his YouTube Channel.
Four Forces Of Flight Lift Weight Thrust Drag
Paper airplane drag, drag definition airplane, drag on an airplane, airplane drag race, drag of an airplane, lift thrust drag gravity paper airplane, airplane drag coefficient, drag bus, arena drag, drag app, how does drag affect an airplane, drag airplane